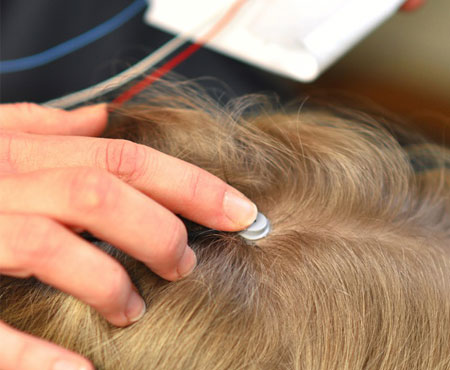
What is Neurofeedback?
Our brains are highly influenced by neuroelectrical activity in terms of communication between different parts of the brain. The brain depends of the effectiveness of neuroelectrical activity and connections like a telephone and computer depend on electricity to function. When our brains are functioning optimally we can easily access or “shift gears,” like the transmission of a car, from different brain wave frequencies and from one part of the brain to another. Problems with neuroelectrical activity are evidenced at times by too much or too little neuroelectrical activity in the brain. We overtly experience physical distress reactions, reduced cognitive functioning and/or emotional terror and despair when this occurs. Overwhelming physiological, cognitive and behavioral symptoms may take over and dominate one’s ability to function.
Neurofeedback is a type of biofeedback. Neurofeedback software provides visual and auditory feedback, to teach the brain how to boost the brain’s innate ability to self-regulate, achieve homeostasis and optimal functioning. Neurofeedback training is a non-invasive treatment in which sensors placed on the scalp monitor an individual’s brain wave electrical activity while immediately comparing these signals with normative databases on a high-speed computer. Using sophisticated computerized programs, patients learn how to both recognize and synchronize brainwave patterns towards normalcy. What we have learned from neurofeedback is that when the brain is given access to itself and information about itself, incredible changes can occur. These changes become relatively permanent by the subsequent neurochemical and physiological changes and “rewiring of the brain” produced by neurofeedback. Neurofeedback software provides visual and auditory feedback, using operant conditioning to teach the brain how to regulate itself. The most obvious comparison is Pavlov’s famous experiment with conditioning dogs (classical condition) wherein meat was used as the reward to change behavior. Neurofeedback uses “rewards” to “condition brain behavior” which in turn “changes human behavior”. There are several kinds of neurofeedback modalities including:
Infraslow Fluctuation Training
Z-score Training
Standardized Low Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography (sLORETA) Training
Conventional Neurofeedback (e.g. Bipolar and 4 channel frequency training, inhibition training, etc.)
pIR HEG (Passive Infrared Hemoencephalography)
Each patient’s neurofeedback protocol is determined by the modality that will best address reducing their symptoms while enhancing brain optimization, their QEEG brain mapping results and their diagnostic evaluation and consultation.
In addition to the success in treating attention deficit and learning disorders, research has supported the efficacy of neurofeedback in benefiting conditions affected by the central nervous system such as anxiety disorders, depression, autistic spectrum disorders, migraine and tension headaches, post-traumatic stress disorders, traumatic brain closed head injuries, chronic fatigue, insomnia, digestive disorders, fibromyalgia, explosive or anger disorders, Tourette’s, tic disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorders.
Specialized Types of Neurofeedback
There are several types of Neurofeedback modalities each with its specific methodology, assessment and purposes at addressing cognitive and behavioral symptoms while enhancing optimal brain functioning. Neurofeedback is not a “one size fit’s all” therapy intervention. Assigning a neurofeedback modality is specific upon an individual’s brain wave morphology (evaluated during the QEEG Brain Mapping procedure) and the targeted neurophysiological symptoms one is experiencing.